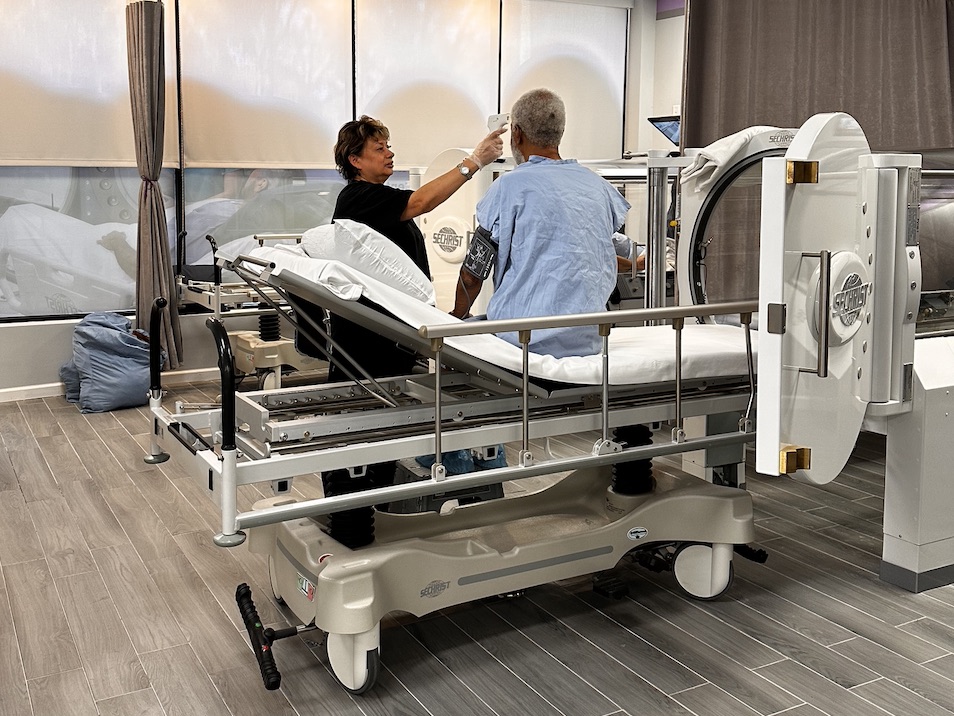
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) has evolved from a mass treatment to a precisely customized therapy for each patient. Medical professionals have shifted their focus from searching for the best, one-size-fits-all protocols to developing personalized plans that maximize treatment outcomes and minimize risks and side effects.
Personalization became a priority after discovering and acknowledging the therapeutic value of breathing pure oxygen at increased atmospheric pressure.
The Foundation of Personalized HBOT
Generally, the HBOT protocols follow unchangeable guidelines. Standard practices commonly involve pressures of 2-3 ATA (atmospheres absolute) for 60-90 minutes. However, some new findings suggest that these standard routines may not be the most effective for all patients and situations.
In principle, personalized HBOT allows for the acceptance that individual features, such as the patient’s age, presence of other illnesses, disease severity, and physiological response patterns, can significantly influence the course of treatment.
Personalizing HBOT begins with a patient’s thorough assessment, which extends beyond the primary diagnosis. Doctors must consider a patient’s cardiovascular condition, respiratory function, the history of the illness, and specific treatment goals. This personalized method enables doctors to adjust the required pressure, treatment time, frequency, and total number of sessions.
Pressure Optimization Strategies
The pressure in HBOT is the most critical parameter in targeted treatment plans. Generally, standard protocols use pressures ranging from 2.0 to 3.0 ATA; personalized ones may require different pressure levels due to specific patient needs and medical conditions. For patients with certain cardiovascular conditions or those who feel uncomfortable at high pressures, lower-pressure protocols may be more suitable; however, the efficacy of the treatment should not be compromised.
At the same time, some experiments demonstrate that particular illnesses respond well to treatments with lower pressure, especially when combined with longer sessions. This can be particularly helpful to aging people, those with health weaknesses, and those who may not be capable of tolerating the physiological stress that comes with higher pressures. On the contrary, people with acute cases like carbon monoxide poisoning or severe infections may choose to go for a higher pressure to get fast therapeutic results.
The main thing in pressure optimization is monitoring and evaluating the patient’s performance. Healthcare professionals observe specific physiological indicators throughout the treatment, including oxygen saturation, blood pressure, and the patient’s comfort scoring. This instantaneous reaction enables dynamic changes in pressure levels throughout the therapy period, ensuring maximum therapeutic results while maintaining patient comfort.
Adapting Treatments
Another central parameter of personalized HBOT plans is the length of treatment. Generally, standard sessions are between 60 and 90 minutes; however, some plans may require significantly different times due to patient-specific factors. Some patients may benefit from shorter and more frequent sessions, while others may require fewer extended treatment periods to achieve therapeutic objectives.
The treatment amount can be adapted; most of the time, it will take the specific treated condition and the patient’s tolerance into account. Longer sessions benefit patients with wound healing problems, as they allow for continuous tissue oxygenation.
Meanwhile, patients treated for neurological issues may find shorter and more frequent sessions more suitable, as the sessions would minimize the potential side effects the patient may experience.
On the other hand, healthcare providers must also consider several practical aspects of duration customization, such as the patient’s scheduling constraints, facility capacity, and insurance coverage limitations. The aim is to find the perfect balance between therapeutic effectiveness and practical feasibility, so patients can still complete their whole course of treatment practically and realistically.
Implementing Clinical Strategies
A planned method is needed to apply personalized HBOT protocols, which starts with a detailed patient evaluation and continues until the treatment is finished. Depending on the patient’s condition, facilities specializing in personalized HBOT usually have teams of multiple disciplines, including hyperbaric doctors, nurses, respiratory therapists, and sometimes wound care specialists or neurologists.
The process usually starts with baseline assessments such as physical examination, detailed medical history review, lab tests, and sometimes imaging studies. The initial protocol outlines pressure levels, session duration, frequency, and the total number of treatments. The patient’s response will be used as a personalization approach, acknowledging that these primary parameters may be decided later.
Regular observation during the therapy period is necessary here. This may involve lengthening the healing of wounds, recovery of neurologic functions, pain alleviation, and improving quality of life in general. Healthcare providers utilize the data they gather at ongoing assessments to make immediate, real-time changes to their treatment, thus ensuring each patient gets the most efficient treatment possible.
Evidence-Based Outcomes
A move to personalized HBOT protocols is supported by increasing evidence that tailor-made regimens can raise treatment results and reduce adverse effects. Research clearly illustrates that patients under customized treatment regimens repeatedly report shorter healing periods, fewer treatment side effects, and a more satisfying care experience.
Research has abundantly demonstrated the merits of personalized treatment regimens for patients with complicated medical conditions or those who have failed to respond positively after using standard protocols. By modulating pressure and duration parameters and basing them on individual patient features, healthcare providers can achieve therapeutic success even in cases where conventional approaches have yielded no results.
The data indicates that personalized HBOT protocols can be more budget-friendly in the long run, even though more frequent monitoring and assessment might be required. Healthcare providers can save money by optimizing treatment parameters for individual patients and reducing the total number of sessions needed while maintaining or improving the therapeutic outcome.
Future Directions and Technology Integration
The future of personalized HBOT can be imagined as a conjunction of advanced monitoring technologies and data analytics that provide real-time feedback on the therapy’s effectiveness. Continuous oxygen monitoring and advanced imaging techniques, including biomarker analysis, provide insight into a patient’s response to therapy.
Innovative technologies, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, are being developed that analyze patient data and predict the best treatment parameters based on individual characteristics and condition-specific factors. This technology will further fine-tune personalized HBOT protocols and improve treatment success for various conditions.
Along with the field’s development, personalized medicine has enormous potential to expand. Some ongoing research directions include investigating new biomarkers that will allow for the most accurate measurement of treatment effectiveness, genetic research that highlights what genes are likely to affect treatment, and how innovative delivery methods will further enhance the patient experience.
Conclusion
Personalized HBOT is the most notable breakthrough in hyperbaric medicine. It moves ahead of generic protocols to adopt individual therapeutic approaches, which optimize pressure and time factors for each patient. This transition exemplifies the broader trend of personalized medicine, acknowledging that the best therapeutic outcomes can be achieved by considering a patient’s unique characteristics.
Evidence and patient satisfaction show that implementing personalized HBOT protocols requires expertise, advanced monitoring capabilities, and commitment to assessment and adjustment throughout the treatment course. However, the investment pays off. According to the evidence, reduced side effects, improved outcomes, and enhanced patient satisfaction are frequently realized.
The increasing advancement of technology and the deepening of our understanding of hyperbaric physiology provide endless opportunities for more sophisticated personalization approaches. The new era of HBOT relies not on general protocols but on carefully designed, individually optimized treatment plans.
___________________________________________________________________________
1659 Ralph Ave., Brooklyn, NY 11236
phone 718-255-9955
fax 718-228-3772
____________________________________________________________________________
References:
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. (2024). Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy. Retrieved from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/hyperbaric-oxygen-therapy
- UCLA Health. Hyperbaric Medicine – Los Angeles, CA. Retrieved from https://www.uclahealth.org/medical-services/hyperbaric
- PMC. A General Overview on the Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Applications, Mechanisms, and Translational Opportunities. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8465921/
- MedStar Health. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy | Wound Healing. Retrieved from https://www.medstarhealth.org/services/hyperbaric-oxygen-therapy